|
Teaching Strategies: Learning Theory SOCIAL COGNITIVE
|
||
|
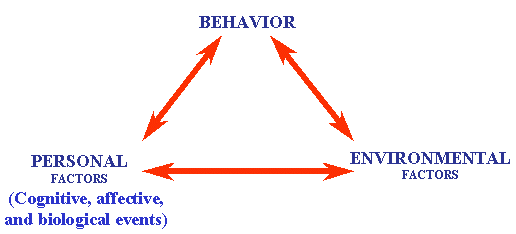
Introduction v So far, we have examined learning theories that focused
either on the environment (Behaviorism) or cognition (Information Processing and
Constructivism). Social cognitive theory attempts to incorporate both the
environment and cognition to explain how people learn . The most important
thing to realize about the theory is that when one aspect of the triangle
above changes, it affects the other parts (notice the arrows go both ways). v So, if you change a student’s belief that she really
can learn the academic content (personal factors – self-efficacy), she
studies longer (behavior), and people
around her tell her what a good student she is (environment), which in turn
reinforces the original starting point (that she can learn the material) and
the cycle continues upward. The same
can happen in a negative way - the student doesn’t believe she can learn the
material, so doesn’t study, and then everyone around her tells her that she
is not a good student, and then the cycle continues downward until the
student gives up trying to learn. v In this assignment, you will apply social cognitive
theory principals to teaching strategies in an effort to help your case study
learn and evaluate the social cognitive theory in the context of your own
personal learning theory. v Student example of this assignment is located in step
6. |
||
|
Instructions |
||
|
Click here to watch
a video on how to do this assignment
|
||
|
Step 1: Describe a teaching
strategy in your standards-based lesson plan that you think supports your
case study’s learning via social cognitive theory. ·
If you
find that the teaching strategy in your lesson plan is missing, not specific
enough, or is lacking in details, then this is a great opportunity to create,
expand, or adapt your lesson instructions and make it better! · For example, in our student lesson plan example from the previous assignment, step number 3 in the writing assignment, the author believes that this supports students’ learning via social cognitive theory: (Note – the author needed to expand his/her instruction by including an example for modeling) ·
The
teacher models how this works by providing examples of how different opinions
can become stronger or weaker just based on what reasons are provided to
support those opinions. (10 minutes) o
Here
is one possible example for the modeling: 1. A person believes that they have been
doing well in school and present the following evidence to his/her parents to
support his/her opinion. 1. Report card shows all A 2. Each teacher writes a testimonial
stating that the student is the best they have ever had in class. 3. The student receives student of the
year for the Nation. 2. Compare the same situation with another
set of evidence to support his/her opinion. 1. Friends all note that student does too
much homework 2. No notes from teachers stating poor
performance 3. Student is convinced that he/she has
turned in all his/her homework. 3. While the student could actually be
doing well in school, only the first set of evidence is convincing enough to
support the opinion because it is based in fact. The other one is based on
other unsound testimonials or lack of facts, which renders the opinion of the
student to just an opinion. §
Teacher
then tells the student that their “Best of…” opinion needs good reasons
supported by facts! ._____________________________________________________________________________ Step 2: Defend why your
teaching strategy will work to support your students’ learning via social
cognitive theory. ·
To get you started in defending your teaching
strategy, consider the following questions as a guide for your thinking, but
you don’t have to address all of them. Please feel free to come up with your
own approaches to help defend your teaching strategy. o
How does your teaching strategy in your lesson… § involve learning through
the environment (social learning theory)? § develop students’
self-efficacy ? § develop students’
outcome expectations? § develop students’
self-regulated learning (self-directed learning)? § Develop
students’ metacognition? ·
Review the resources below to provide you with
the research behind the defense of your teaching strategy. You are welcome to
use your own resources via other text, internet, etc., as long as you provide
valid citations of where you got your answer.
·
For example, in our student lesson plan
example, here is how the author defends that the writing activity supports
students’ learning via social cognitive theory: o
According
to the Woolfolk text, social cognitive theory helps students learn through
vicarious learning, or modeling. This modeling is known as social learning
theory and was an early version of social cognitive theory, which later
added in the cognitive portion to its theory. This teaching strategy of
modeling supports students’ learning because according to social learning
theory, learning can occur by just observing the behavior of others and the
outcomes of those behaviors. This is drastically different from classical and
operant conditioning which claimed that all learning needs to have immediate
consequences for behavior to be reinforced and permanently changed. Social
learning theory claims that modeling can reinforce the behavior, without any
actual behavior from the observing person as long as the model and the
outcomes from the model’s behavior are valued. The observer remembers the
modeling and will change his/her behavior when the same situation occurs down
the road. According to the Brain Fact’s website, this ability to remember
what a model does is supported by the discovery of “mirror neurons” in the
brain. These mirror neurons become active whenever modeling occurs and
“mirror” that modeling in our own brains. This
neurons help us remember what we observed and help us act out that behavior
later on. o
By
having the teacher demonstrate how to support an idea with facts versus only
using opinion allows students in the class to observe how to do that
behavior. If students view the teacher as being a relatable model and the
students value the outcome of doing the behavior, then students’ will most
likely learn the behavior to be used at a later time. Brain Facts website: http://www.brainfacts.org/brain-basics/neuroanatomy/articles/2008/mirror-neurons/ ___________________________________________________________________________ Step 3: Choose a social cognitive teaching strategy below that you think helps students learn best and explain why you think it is the best strategy. This strategy should be different from the social cognitive teaching strategy already identified and described previously in step 1 and 2. · All of these social cognitive teaching strategies can be found in the Woolfolk text in Chapter 11 (12th edition) and Chapter 10 (11th edition)
·
For example, here is how the author in the
student example might answer: o A teaching strategy that I plan to use with my students to help them reach the benchmark is through developing students’ sense of self-efficacy. According to the Woolfolk text, self-efficacy develops whenever students believe that they can do an academic task. The best way to get students to believe that they can do something is to provide them with real success on previous classroom tasks before they do the task. So, if I want to get my students to believe that they can write an opinion paper with good factual supporting evidence, then I have to provide them with opportunities to show that they can do it. These opportunities have to be within the students’ ability and have to include specific feedback that will let the students know how they are doing. _____________________________________________________________________________ Step 4: Based on the teaching strategy chosen above, incorporate that strategy into your standards-based lesson plan instruction. · For example, here is how the author in the student example might answer: ·
Lesson
#5: Students write their opinion paper with supporting facts and receive
feedback from teacher, peers in homogeneous groups, and do a self-assessment
on their paper using the assessment rubric developed for this assignment.
Students then rewrite their paper. o
Teacher
should provide specific feedback and solutions that addresses the paper and
should not be directed towards the students’ ability. 1. For example teachers should try to
state, “In paragraph 2, the supporting evidence represents an opinion and
needs a fact to back it up. Consider reviewing the brainstorming activity
notes and listing all the possible reasons that can be used to support the
opinion. Then please go through the list separating fact from opinion. Use
the teacher or a peer to help, if needed. Then once a fact is identified,
research the fact, and include it in the second paragraph. 2.
The
teacher should avoid stating, “In paragraph 2, you backed up your thesis
using only your opinion and that is wrong. You need to find some facts to
back it up. _____________________________________________________________________________ Step 5: Choose a social cognitive theory teaching strategy above that you think doesn’t help students learn and explain why you think that this strategy is ineffective. ·
For example, here is how the author in the
student example might answer: o
I think
that self-regulated learning strategies of making the students organize their
materials are often not very effective. Although it is very important for
students to be organized, it is very difficult to motivate students to do so.
According to social cognitive theory, students change their behavior when
they feel they can do the task, the outcomes for doing the task are valuable,
and that the learning environment encourages doing the task. The problem lies
in the fact that students see very little value for organizing their work for
the effort put in. Even if the teacher gives a grade for their organization,
students then will put in the effort just before the grade, and then go back
to their old behavior. It is much like when parents want their child to clean
up their room. The only way for
students to be self-regulated in their organizational skills (by the way,
this is GLO #1 for self-directed learning in the dept. of education in
Hawai`i), the teacher would have to find something that makes it valuable
enough for students to constantly try and organize their work. This is very
difficult to find and that is why it is not a very effective teaching
strategy. Good in theory, difficult in practice. ________________________________________________________________________ |
||
|
Step 6: Present and communicate
your answers electronically and place
in your standards-based lesson plan at the end of Part II (after your lesson
instructions). ·
Although a majority of you will defend your
teaching strategy by writing a paragraph, there may be a few of you that may
want to use other alternative media, and I want to support that and give you
options to be creative. You may also use a combination of media to make your
point. For example, you may combine some writing, with images, podcast,
YouTube Video, PowerPoint, etc., to defend your teaching strategy. ·
Keep in mind that any presentation method is
valid as long as it clearly communicates and supports your answer. My only
criteria for the type of media used is that the media is electronic and can
be placed or linked successfully from your lesson plan. ·
After you have completed your answers, then
place it at the end of your standards-based lesson plan at the end of Part 2:
Guiding the Learning (after your
lesson instructions). Place a heading above your answer – Teaching
Strategies: Learning Theory - Social
Cognitive Theory ·
See student
example #1 as a model (go to the end of the lesson in Part 2: Guiding the
Learning to view). · When finished, upload the entire lesson plan (with all four sections) to Laulima Assignments by the due date. |

![Description: MCj04348740000[1]](learning_social_cognitive_files/image004.gif)