THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT
Geography 101
ToC
LIFE
Animals
Biomes
Tropics
Temperate
Cold
Hawai'i
Terrestrial Biomes
|
|
BOX 1 |
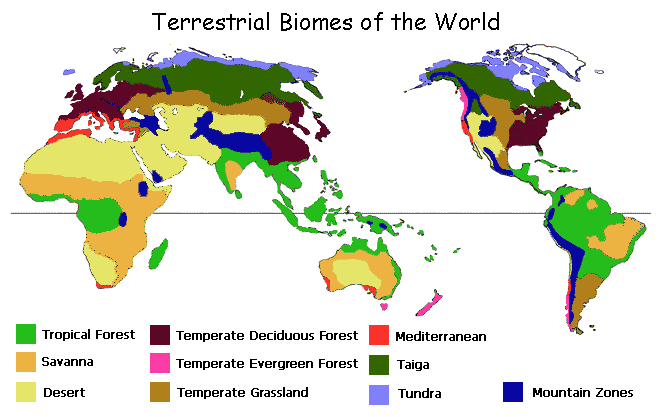
A vegetation zone, or terrestrial biome, is a recognizable community of plants that have adapted to conditions in a particular area. It should be noted at the outset that this chapter refers to natural vegetation, which in many areas no longer exists. Most of the temperate deciduous forests have been cleared for agriculture, for example, and most of the tall grass prairie has been plowed under and replaced with cereal grains like wheat and barley. The word terrestrial distinguishes our focus in this chapter from another major ecotype, marine biomes, which we will not discuss.
The world's terrestrial biomes are determined mainly by climate. At a basic level, most of Earth's land area can be called either forest, grassland, or desert. These vegetation types are a response to moisture availability. If an area is always wet, forest will grow. If there are long dry seasons with substantial moisture deficits, grassland will dominate. If there is no appreciable wet season at all, desert results.
always wet |
wet and dry seasons |
always dry |
forest |
grassland |
desert |
To a lesser extent, vegetation communities reflect other environmental variables as well, particularly temperature. For purposes of illustration and discussion, vegetation zones separate conveniently into tropical biomes (always warm), temperate biomes (warm and cold seasons), and cold region biomes, all of which are shown in the figure below. We will be referring to this figure many times in the next few sections with an overview of each category.