THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT
Geography 101
ToC
MAPS
Geography
Size
Latitude
Longitude
Time
Maps
New Tools
Size
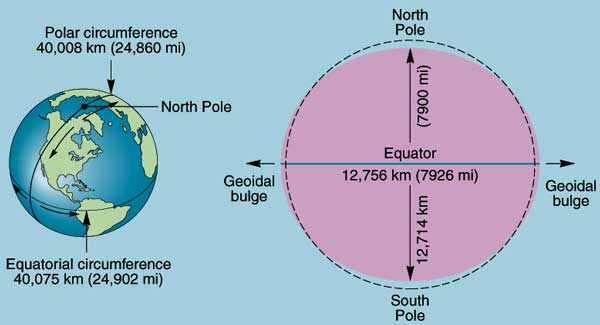
We inhabit a tiny life zone at the boundary between an enormous, lifeless sphere of rock, nickel, and iron and the vacuum of space. That sphere, our planet, is about 13,000 kilometers (8000 miles) in diameter and 40,000 kilometers (25,000 miles) in circumference. More accurate dimensions are shown below.
|
|
BOX 1 |
Because the Earth spins on its axis once a day, centrifugal force causes it to flatten somewhat, making the equatorial diameter larger than the polar diameter. This gives Earth a slightly oblate shape. For example, if you stood at the North Pole, you would be about 34 km (21 miles) closer to the center of the Earth than if you stood at sea level on the Equator.
Earth's oblateness and other deviations from a perfect sphere make precision mapmaking a complicated task. The science of geodesy provides the necessary precision through a detailed mathematical description of Earth's shape. Geodesy has become an extremely important tool in the modern era of determining location through satellite measurements.
The immense size of the planet can be difficult to relate to in terms of everyday experience. Perhaps we understand travel time better than physical distance. For example, the first sailing circumnavigation of the globe by Ferdinand Magellan's crew in an old square rigger completed in 1522 took over three years. A couple of runners have globetrotted Earth's equatorial distance in less than 2 years. The current circumnavigation sailing record, set in a giant trimaran, is 41 days. A supersonic aircraft, an Air France Concorde, set the east-west flying record at just under 32 hours and the International Space Station orbits the earth every 92 minutes. While Earth's size remains physically unchanged, in terms of human perception and travel time, our planet is shrinking rapidly.
In the next sections, we discuss the standard international coordinate system for the Earth: latitude and longitude.